Introduction
Addrmatcher is an open-source Python software for matching input string addresses to the most similar street addresses and the geo coordinates inputs to the nearest street addresses. The result provides not only the matched addresses, but also the respective country’s different levels of regions for instance - in Australia, government administrative regions, statistical areas and suburbs in which the address belongs to.
The Addrmatcher library is built to work with rapidfuzz, scikit-learn, pandas, numpy and provides user-friendly output. It supports python version 3.6 and above. It runs on all popular operating systems, and quick to install and is free of charge.
In this initial release, the scope of input data and matching capability are limited to Australian addresses only. The Addrmatcher library will see the opportunity to scale the matching beyond Australia in future.
- The package offers two matching capabilities
address-based matching accepts string address as argument.
coordinate-based matching takes geo coordinate (latitude and longititude) as input.
The development team achieved the optimal speed of matching less than one second for each address and each pair of coordinate input.
The reference dataset is built upon GNAF(Geocoded National Address File) and ASGS(Australian Statistical Geography Standard) for the Australian addresses. The package users will require to download the optimised format of reference dataset into the working direcory once the package has been installed.
Installation
pip install addrmatcher
Data Download
Once the package has been installed, the reference dataset needs to be downloaded into the local current project working directory prior to implementation of the package’s matching functions.
In the command line interface, .. code-block:
addrmatcher-data aus
The above console script will download the dataset which is currently hosted in Github into the user’s directory. addrmatcher-data takes an argument, country. By default, the country is Australia which is indicated by aus. Then Australia address files will be downloaded. After executing the command, the 37 parquet files will be stored in directories for example /data/Australia/*.parquet.
Package and Classes Import
# Import the installed package
from addrmatcher import AUS, GeoMatcher
# Initialise the geo region as AUS
matcher = GeoMatcher(AUS)
Example - Address Matching
matched_address = matcher.get_region_by_address("9121, George Street, North Strathfield, NSW 2137")
print(matched_address)
> {'SA4_NAME_2016': ['Sydney - Inner West'],
'LGA_NAME_2016': ['Canada Bay (A)'],
'SA3_NAME_2016': ['Canada Bay'],
'RATIO': [100.0],
'STATE': ['NSW'],
'FULL_ADDRESS': ['9121 GEORGE STREET NORTH STRATHFIELD NSW 2137'],
'SA2_NAME_2016': ['Concord West - North Strathfield'],
'SSC_NAME_2016': ['North Strathfield'],
'MB_CODE_2016': ['11205258900'],
'SA1_7DIGITCODE_2016': ['1138404']}
Example - Coordinate Matching
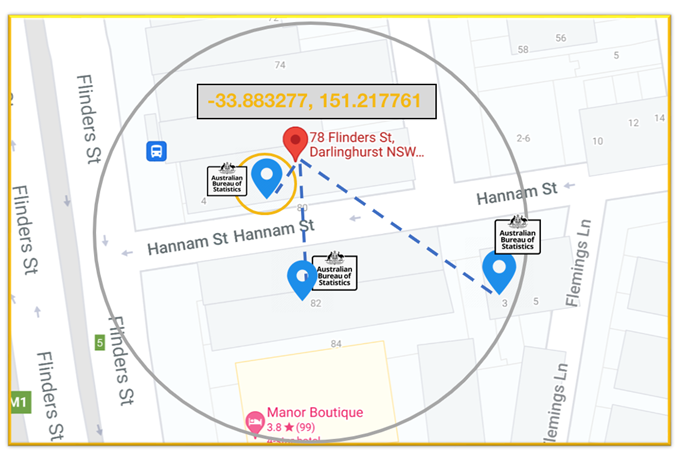
nearest_address = matcher.get_region_by_coordinates(-29.1789874, 152.628291)
print(nearest_address)
>{'IDX': [129736],
'FULL_ADDRESS': ['3 7679 CLARENCE WAY MALABUGILMAH NSW 2460'],
'LATITUDE': [-29.17898685],
'LONGITUDE': [152.62829132],
'LGA_NAME_2016': ['Clarence Valley (A)'],
'SSC_NAME_2016': ['Baryulgil'],
'SA4_NAME_2016': ['Coffs Harbour - Grafton'],
'SA3_NAME_2016': ['Clarence Valley'],
'SA2_NAME_2016': ['Grafton Region'],
'SA1_7DIGITCODE_2016': ['1108103'],
'MB_CODE_2016': ['11205732700'],
'STREET_NAME': ['CLARENCE'],
'STREET_TYPE_CODE': ['WAY'],
'LOCALITY_NAME': ['MALABUGILMAH'],
'STATE': ['NSW'],
'POSTCODE': ['2460'],
'ADDRESS_DETAIL_PID': ['GANSW706638188'],
'FILE_NAME': ['NSW-10.parquet'],
'DISTANCE': [6.859565028181215e-05]}
How the Address Matching Works?
1. Address-based matching
The idea behind the address-based matching function is comparing the similarity between two addresses. The more similar the strings are, the more likely both addresses are identical. Therefore, the package adopted the edit-distance method (Levenshtein, Jaro, and Jaro-Winkler) to quantify text similarity based on the minimum number of operations required to transform one string to the other. The package performs address matching by comparing the similarity of the input address with the reference dataset. The function then returns the address and its corresponding regional level that has the highest similarity ratio.
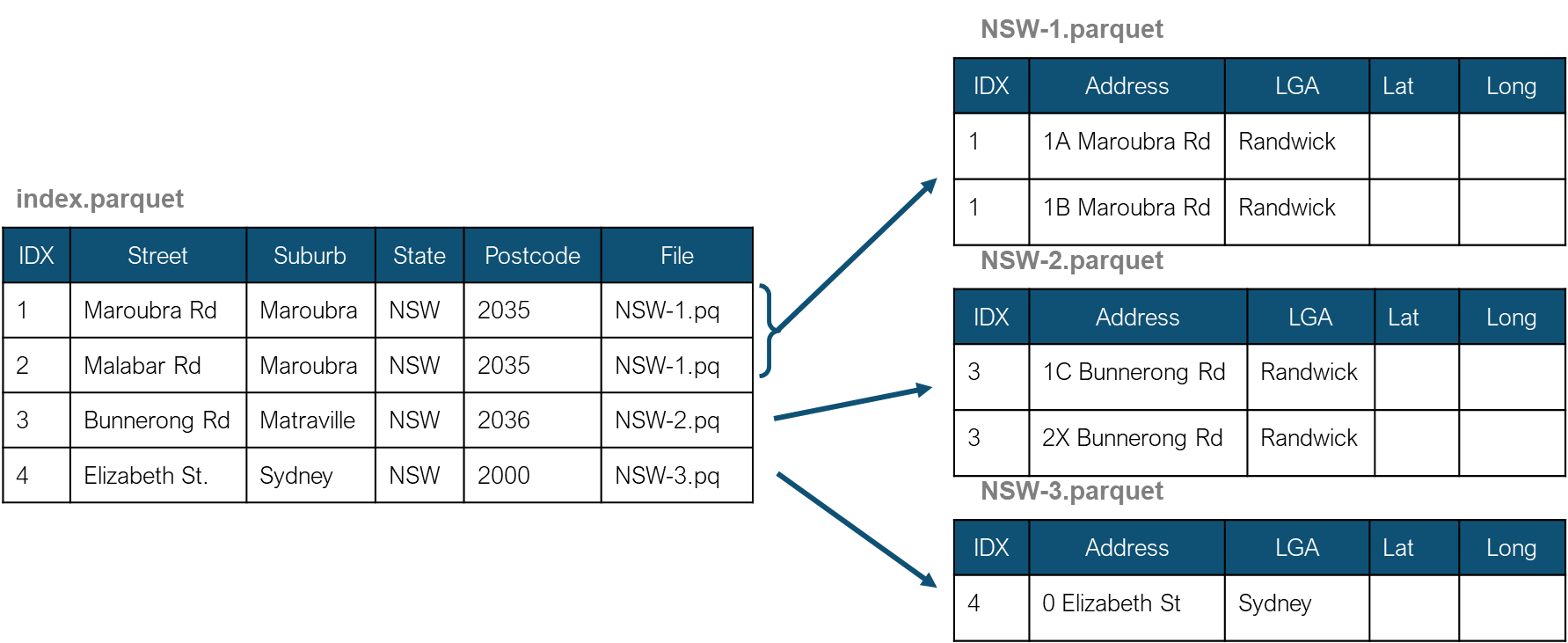
An index file was created to store the unique combination of the street name, locality, state, and postcode. The index file keeps the distinct physical addresses without street numbers, lot numbers, and other similar attributes. Also, the complete addresses were divided into multiple files to limit the number of rows in each file below 500,000 addresses. The index file then stores the filename of the full physical address location.
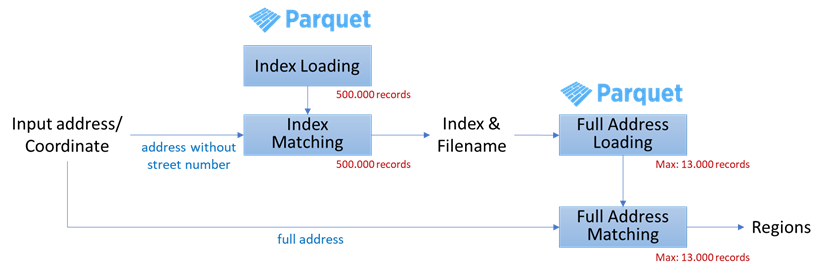
With this file structure, the package does not need to load all 15 million records and compare the input address with the entire list of addresses. Instead, the package only needs to load the index file and match the combination of street, suburb, state and postcode from the input address with composite of those in the index file. Then, the matched combination of street, suburb, state and postcode gets the name of the respective address file to load into the memory.After that, string matching is performed between the input address and the addresses in the file. Therefore, the package only needs to load and match the small factional of the entire dataset.
2. Coordinate-based matching
Coordinate-based matching is distance-based matching. The matching is performed by searching for closer addresses in the GNAF dataset to the input geo-coordinates based on geo-distances.